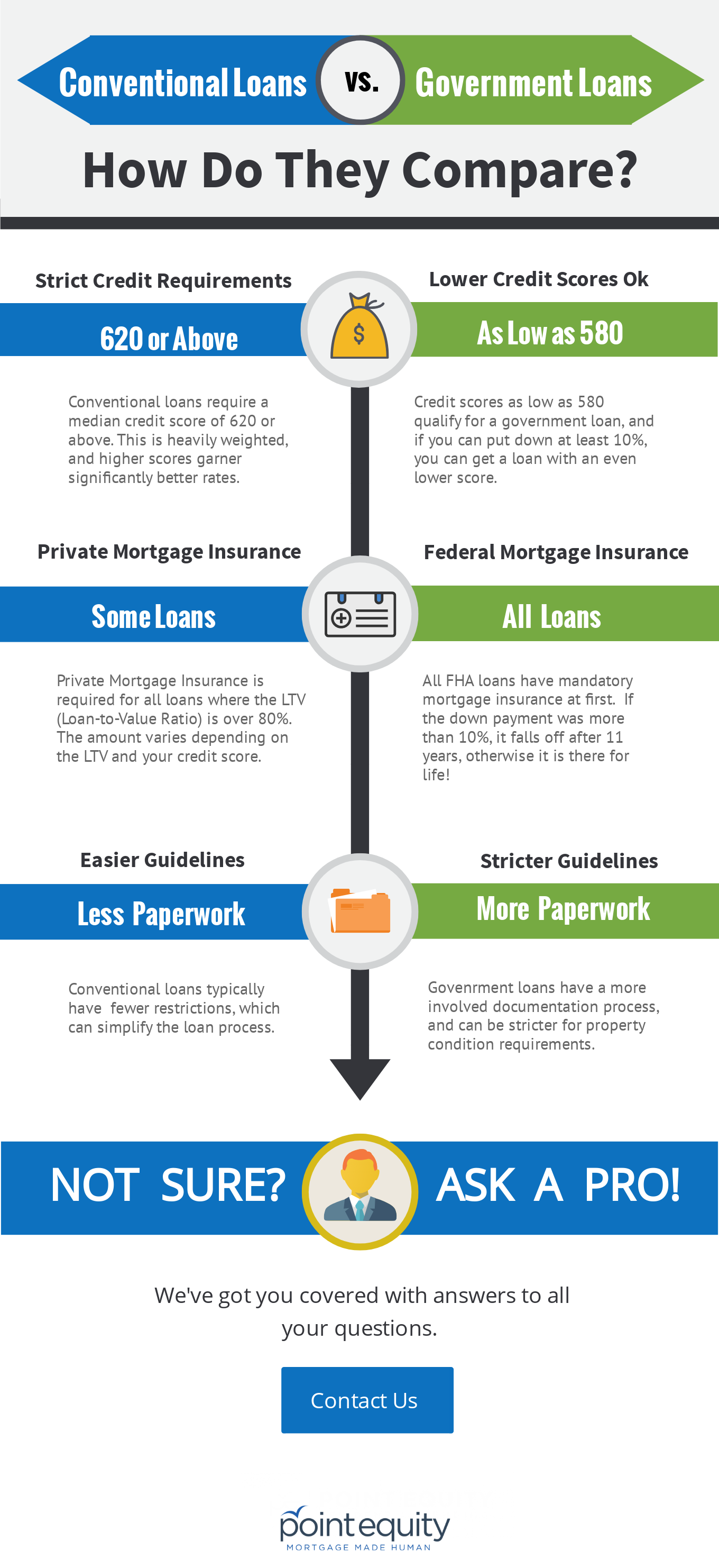
Summarize the Differences Between Conventional Loans and Government Loans
Rising house prices created the belief that prices would continue. For purposes of subpart 329 only all payments made under the clause at 52232-5 Payments Under Fixed-Price Construction Contracts and the clause at 52232-10 Payments Under Fixed-Price Architect-Engineer Contracts.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/whats-difference-between-fha-and-conventional-loans_final-ede6be99eeb344c0860e12ba19c41bff.png)
Fha Loans Vs Conventional Loans What S The Difference
They were able to fund these subprime loans by packaging them into financial derivatives which banks and financial institutions across the world were eager to buy.

. Final cost or fee payments where amounts owed have been settled between the Government and the contractor. Lenders with nominal assets will lose. Those with mortgages on fixed nominal interest rate loans for example will benefit from inflation because the debt stays the same in nominal terms and so becomes smaller in real terms.
Rising house prices in the US in the 2000s were driven by the behaviour of lenders encouraged by government policy to extend loans to poorer households. And Interim payments under a cost. Borrowers with nominal debt will benefit.
Banks or others who have loaned money at fixed nominal interest rates will lose because when the sum is repaid it.

A Comparison Between Conventional And Government Issued Loans Al Com
/whats-difference-between-fha-and-conventional-loans_final-ede6be99eeb344c0860e12ba19c41bff.png)
Fha Loans Vs Conventional Loans What S The Difference

A Comparison Between Conventional And Government Issued Loans Al Com
No comments for "Summarize the Differences Between Conventional Loans and Government Loans"
Post a Comment